Ad
Ad
Carbon Farming in India: Sustainable Agriculture for Climate Change Mitigation and Soil Health

Climate change is one of the most significant challenges the world is facing today. The agriculture sector, which plays a crucial role in contributing to and mitigating environmental impacts, is exploring innovative solutions such as carbon farming. Carbon farming is a method that involves sequestering carbon from the atmosphere and storing it in the soil, plants, and trees. This practice not only helps in combating climate change but also improves soil health, increases agricultural productivity, and offers new economic opportunities to the farmers.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of carbon farming, its significance, benefits, challenges, and the role of various governmental schemes in promoting the sustainable agriculture in India.
What is Carbon Farming?
Carbon farming is a set of agricultural practices thats aimed at increasing the amount of carbon stored in the soil and vegetation. Techniques such as no-till farming, cover cropping, agroforestry, and composting help capture carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and store it in the soil. This process improves the fertility of the soil, enhances crop yields, and also contributes in the fight against climate change by reducing the greenhouse gas emissions.
Significance of Carbon Farming
- Climate Change Mitigation: Carbon farming plays a crucial role in addressing climate change by sequestering the carbon in soil and reducing the effect of greenhouse gas emissions.
- Soil Health Enhancement: Practices such as conservation tillage and organic farming improve soil structure, increase moisture retention, and also enhances the availability of nutrients to the crops, leading to a higher agricultural productivity.
- Biodiversity Enrichment: Carbon farming promotes biodiversity by creating complex ecosystems within agricultural landscapes. It attracts the beneficial insects and pollinators, strengthens crop resilience against diseases, and reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
- Economic Opportunities: Farmers can participate in carbon credit markets for earning an additional income by implementing the practices of carbon farming. This diversification of revenue sources strengthens the financial resilience and also contributes to the sustainability of farming operations.
- Water Conservation: Carbon farming techniques improve the soil's water-holding capacity, reducing the need for frequent irrigation and contributing to water conservation efforts.
Also Read: Top 10 Most Profitable Farming Ventures in India
Top 9 Government Schemes Supporting the Carbon Farming in India
The Indian government has introduced several initiatives and incentives to promote sustainable agricultural practices, including carbon farming. Here are some of the key government schemes related to carbon farming:

1. National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Overview: NMSA is part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and focuses on promoting sustainable agriculture by improving soil health, water usage efficiency, and organic farming.
- Incentives: Farmers receive financial assistance and subsidies for adopting climate-resilient technologies, soil management practices, and water conservation methods, which are essential components of carbon farming.
2. Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY)
- Overview: PMKSY aims to enhance water use efficiency in agriculture and ensure that every farm has access to water.
- Incentives: The scheme promotes micro-irrigation systems like drip and sprinkler irrigation, which are crucial for maintaining soil moisture and supporting carbon farming practices. Farmers can avail subsidies for installing these systems.
3. Soil Health Card Scheme
- Overview: This scheme provides farmers with soil health cards that include recommendations on appropriate fertilizers and soil management practices.
- Incentives: By promoting the balanced nutrient management and organic farming, this scheme indirectly supports carbon farming practices, leading to better soil carbon sequestration.
4. Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY)
- Overview: RKVY is a state-led scheme aimed at increasing public investment in agriculture and allied sectors.
- Incentives: The scheme provides financial support for projects related to sustainable agriculture, including agroforestry, conservation tillage, and organic farming, which are integral to carbon farming.
5. Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
- Overview: PKVY promotes organic farming across India and supports farmers in adopting eco-friendly farming practices.
- Incentives: Farmers receive financial assistance for inputs like organic fertilizers and bio-pesticides, which contribute to carbon farming by enhancing soil health and reducing the dependency on the chemicals.
6. National Agroforestry Policy
- Overview: The National Agroforestry Policy encourages the integration of trees and shrubs into agricultural lands to improve biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Incentives: The policy provides financial and technical support to farmers adopting agroforestry practices, which are a key component of carbon farming.
7. Sub-Mission on Agroforestry (SMAF)
- Overview: SMAF is part of the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture and promotes tree plantation on farmland.
- Incentives: The program provides subsidies and financial support for planting trees on agricultural lands, which helps in carbon sequestration and improves the overall sustainability of farms.
8. Green India Mission
- Overview: As part of the NAPCC, the Green India Mission focuses on increasing the forest cover and promoting sustainable forest management.
- Incentives: The mission supports activities like reforestation and afforestation, which contribute to carbon sequestration and are aligned with the goals of carbon farming.
9. Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP)
- Overview: MKSP is a sub-component of the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) aimed at empowering women farmers.
- Incentives: The program promotes sustainable agricultural practices, including organic farming and agroforestry, by providing training, financial support, and access to resources for women farmers.
Also Read: Top 21 Central Government Schemes for the Welfare of Farmers in India
Challenges of Carbon Farming in India
While carbon farming offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges:
- Soil Composition: - Soils with poor structure or low organic matter may have limited capacity for carbon storage, necessitating alterations or management practices for enhanced fertility and carbon sequestration potential.
- Geographic Location: - Geographic factors like elevation, slope, and proximity to water bodies impact the options of land usage and agricultural productivity. High-altitude regions may have limited crop options, while coastal areas may face challenges related to saltwater intrusion and soil salinity.
- Varieties of Crops: - Selecting the right crop varieties that are suitable for the specific types of soil, climates, and growing seasons is quite critical for optimizing the agricultural productivity and the carbon sequestration potential. Limited availability of diverse crop varieties or lack of access to improved seeds may limit the farmer’s ability to maximize the benefits of carbon farming.
- Water Scarcity: - Adequate water is needed for the plants growth and photosynthesis, which is the fundamental process for the carbon sequestration. Dry regions face challenges in carbon farming due to inadequate availability of water.
- Financial Constraints: - Small-scale farmers often encounter financial barriers, struggling to afford the initial cost that’s associated with implementing the sustainable practices essential for carbon farming.
- Limited Policy Support: - The absence of robust policy frameworks and insufficient community engagement also hinders the widespread adoption of carbon farming practices, restricting its potential impact on mitigating climate change.
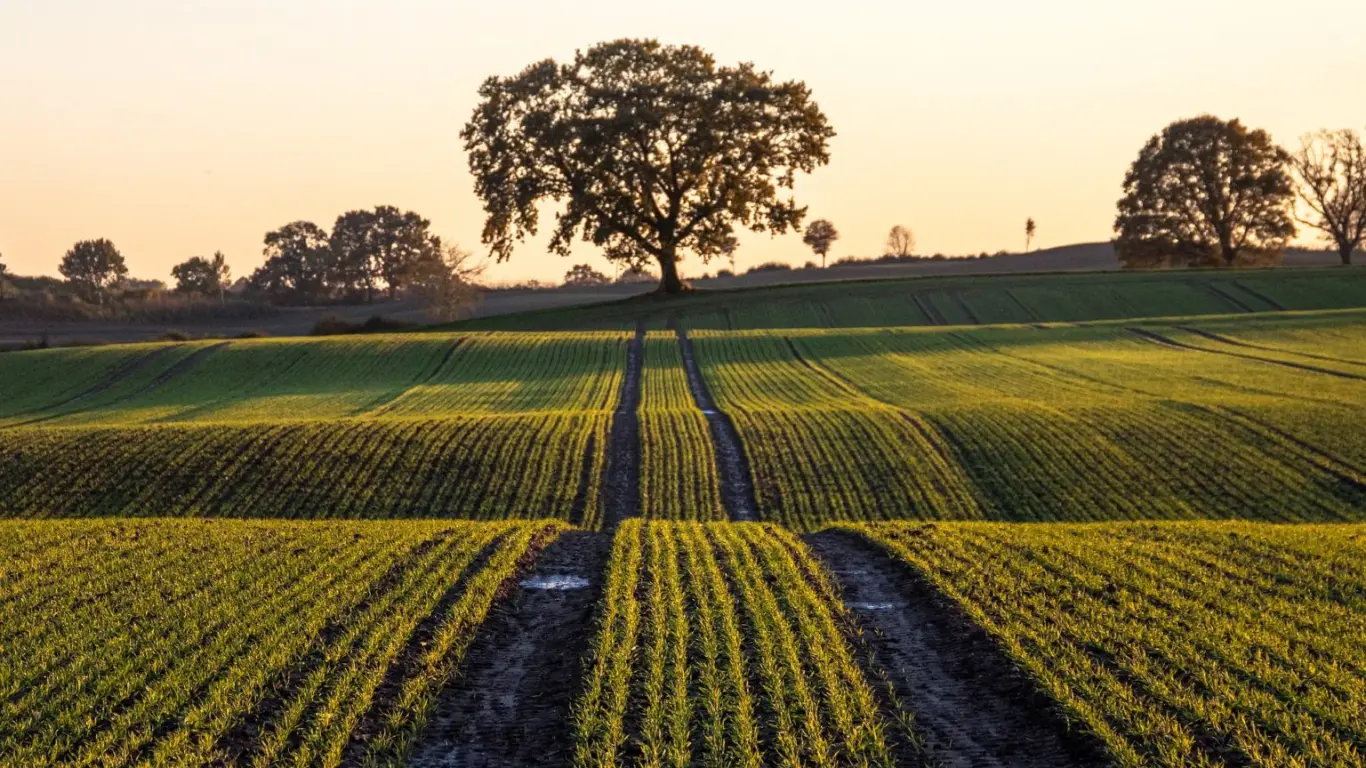

Strategies to Promote Carbon Farming in India
To overcome these challenges and encourage the adoption of carbon farming, the following strategies can be considered:
- Strengthening Legal Frameworks: - Enacting comprehensive carbon farming legislation can promote the creation of carbon sinks on agricultural lands. This approach can address the climate crises, improve agricultural sustainability, and also promote equitable development.
- Providing Direct Incentives: - Recognizing the pivotal role of the agriculture sector in carbon capture, it is imperative to provide direct incentives, such as tools and credit support, for adopting climate-friendly practices. Existing policies should be enhanced to significantly incentivize the expansion and preservation of carbon sinks.
- Utilizing Carbon Credits and Banks: - Rewarding farmers with globally tradable carbon credits and establishing the carbon banks can incentivize the carbon sequestration efforts. These mechanisms can also facilitate the sales of credits to corporations seeking emission offsets, thus promoting sustainable land management.
- Promoting Collective Engagement: - A successful framework for carbon farming requires unified policies, public-private collaborations, precise quantification methods, and supportive financing mechanisms. Implementation at a scalable level is also crucial for achieving measurable carbon capture while ensuring the soil health and resilience.
- Unlocking Soil Potential: - Soil is a potent carbon sink and a vital component of carbon farming. India must harness this potential to meet its Net Zero goals and pursue decarbonization.
Also Read: Organic Farming in India: Types, Methods, Benefits & Challenges Explained
CMV360 says
Carbon farming represents a promising pathway to making India's agricultural sector more sustainable. By adopting carbon-neutral farming practices, Indian farmers can contribute significantly to mitigating climate change while improving soil health and enhancing agricultural productivity.
With the support of government schemes and initiatives, farmers can access the resources and incentives needed to implement carbon farming effectively. However, for widespread adoption, increased awareness, robust policy frameworks, and a functional carbon credit market are essential. With the right support, India can lead the way in sustainable agriculture and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
नवीनतम लेख
Comprehensive Guide to Tractor Transmission System: Types, Functions, and Future Innovations
Learn about tractor transmission types, components, functions, and selection factors to enhance efficiency, performance, and agricultural productivity....
12-Mar-25 09:14 AM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंModern Tractors and Precision Farming: Transforming Agriculture for Sustainability
Precision farming enhances agriculture by integrating GPS, AI, and modern tractors for sustainable, efficient, and productive farming practices in India....
05-Feb-25 11:57 AM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंTop 10 Tractors Under 30 HP in India 2025: Guide
Top 10 tractors under 30 HP in India offer efficiency, affordability, and power, ideal for small farms with diverse agricultural needs....
03-Feb-25 01:17 PM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंNew Holland 3630 TX Super Plus vs Farmtrac 60 PowerMaxx: Detailed Comparison
Compare New Holland 3630 and Farmtrac 60 tractors by specs, price, and features to find the perfect fit for your farm....
15-Jan-25 12:23 PM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंSwaraj 735 FE Vs Eicher 380 2WD Prima G3: Detailed Comparison
The Swaraj 735 FE and Eicher 380 2WD Prima G3 are reliable, powerful tractors suited for various farming tasks....
14-Jan-25 09:41 AM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंHow to Choose the Perfect Tractor for Your Farm: A Comprehensive Guide
Choose the right tractor by assessing farm needs, horsepower, efficiency, comfort, and budget to enhance productivity and savings....
09-Jan-25 09:43 AM
पूरी खबर पढ़ेंAd
Ad
As featured on:


पंजीकृत कार्यालय का पता
डेलेंटे टेक्नोलॉजी
कोज्मोपॉलिटन ३एम, १२वां कॉस्मोपॉलिटन
गोल्फ कोर्स एक्स्टेंशन रोड, सेक्टर 66, गुरुग्राम, हरियाणा।
पिनकोड- 122002